Manage EPM-UL Policies
The Policy section allows you to manage creating, updating, and deleting Endpoint Privilege Management for Unix and Linux(EPM-UL) policy types:
- Role-based policy
- Script-based policy
- File Integrity Monitoring (FIM) policy
- Endpoint Privilege Management for Networks policy
- Sudo policy
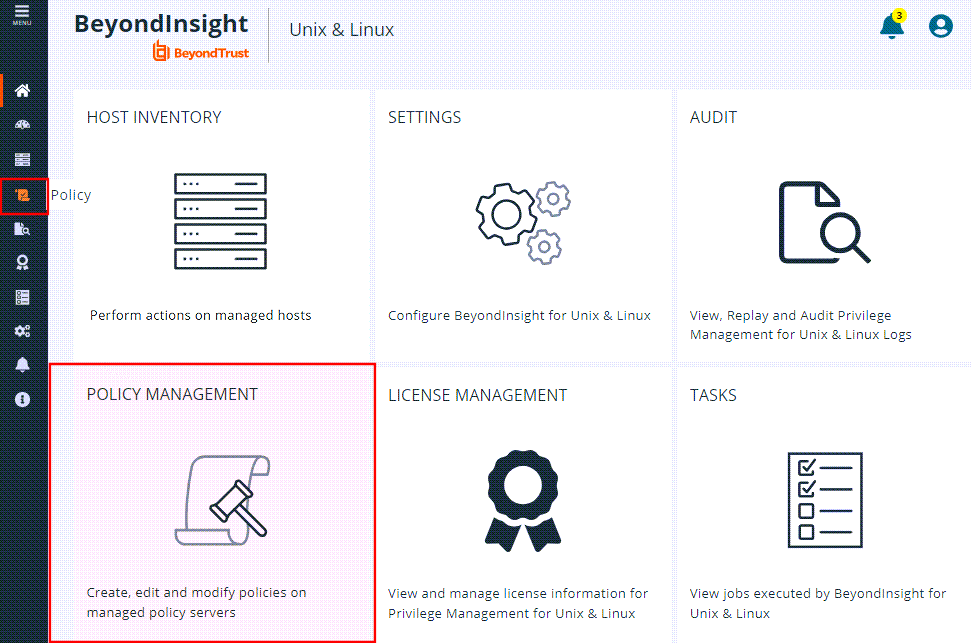
To access the Policy page, from the Home page, click either the Policy Management tile or the Policy icon on the main menu on the left.
View Server Details
To locate a server and view the server details, you can filter hosts by Hostname, IP Address, and Tags. The policy server list is made of known policy servers with working REST connections. If a server is listed in gray, the server has an unsupported version of EPM-UL installed and must be upgraded to enable policy management.
To view server details:
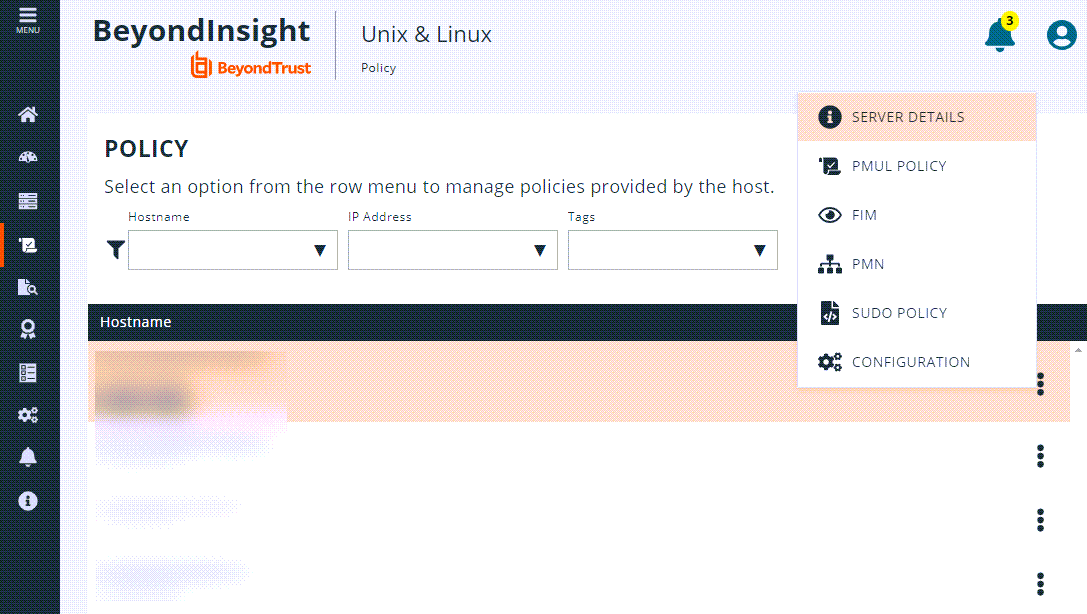
- Go to the Policy page.
- In the Hostname list, select a server entry, and then at the far right, click the vertical ellipsis menu icon and select Server Details.
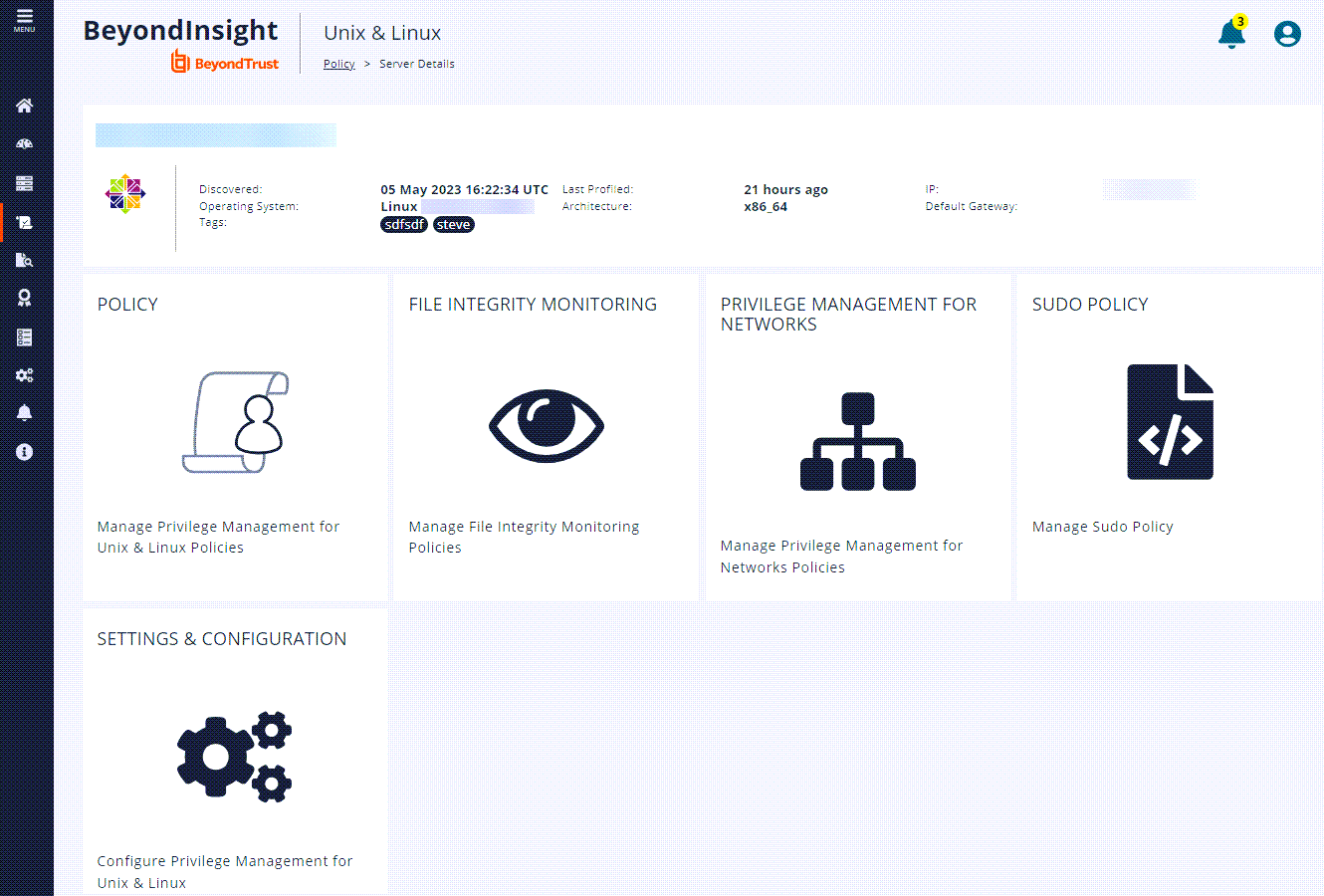
The server details are listed at the top, and you can click any of the tiles below to access a policy type to manage.
Manage a Policy
To manage policies, you must select the policy server on which the policy resides, and then choose the type of policy you wish to manage.
To select a policy server and policy to manage:
- Go to the Policy page.
- In the Hostname list, select a server entry, and then at the far right, click the vertical ellipsis menu icon and select which type of policy you want to manage.
- You can also access the different policy types by clicking the tiles on the Server Details page.
If the host is configured as a client in the Registry Name Service, you must edit policy on the primary registry server.
Role-Based vs. Script-Based Policies
an EPM-UL policy server is either in role-based or script-based policy mode. A server in role-based mode only uses role-based policy and ignores all script policies. A server in script-based policy mode only uses script policies.
When accessing the Policy management page for a selected host, the landing page indicates the policy mode the host is using: role-based or script-based. To change the policy mode from one to the other, click the Settings & Configuration tile, and go to Endpoint Privilege Management for Unix and Linux Policy Settings.
Manage Policy Server Mode
To manage a script policy on a server which is in role-based mode, you can switch the server mode. You can also switch from script-based policy mode to role-based mode.
Switching modes disables the previously configured mode and policies are no longer available to requesting clients. Policies are not removed when switching modes. This option can be changed at any time.
To manage Policy Server mode:
- Go to the Policy page.
- In the Hostname list, select a server entry, and then at the far right, click the vertical ellipsis menu icon and select Configuration.
- Click the Endpoint Privilege Management for Unix and Linux Configuration tab.
- In the Policy Mode section, click Enable Script Based Policy or Enable Role Based Policy to enable the preferred policy mode.
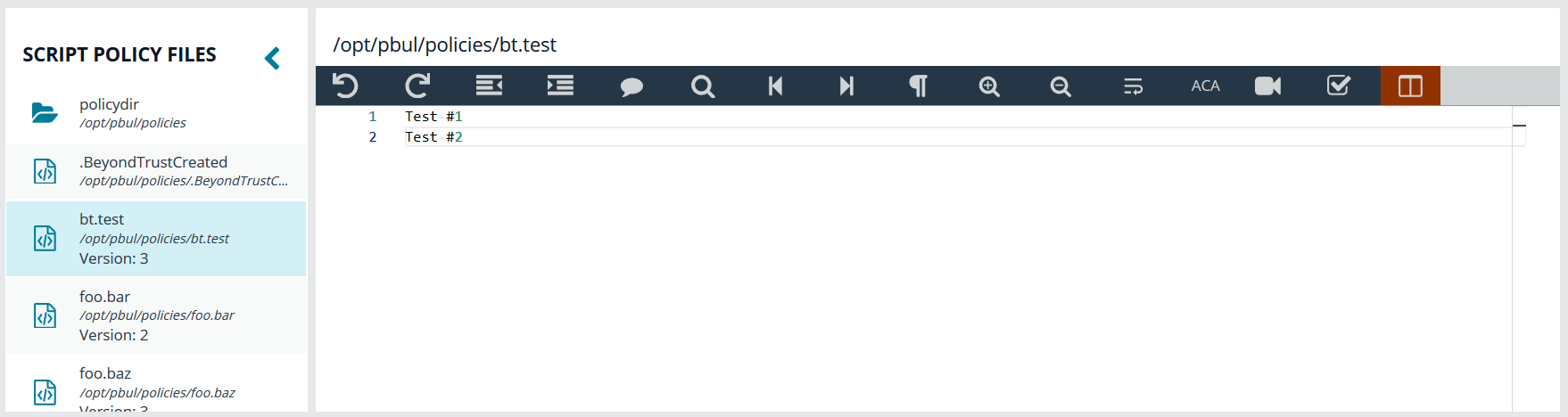
BeyondInsight for Unix & Linux Code Editor
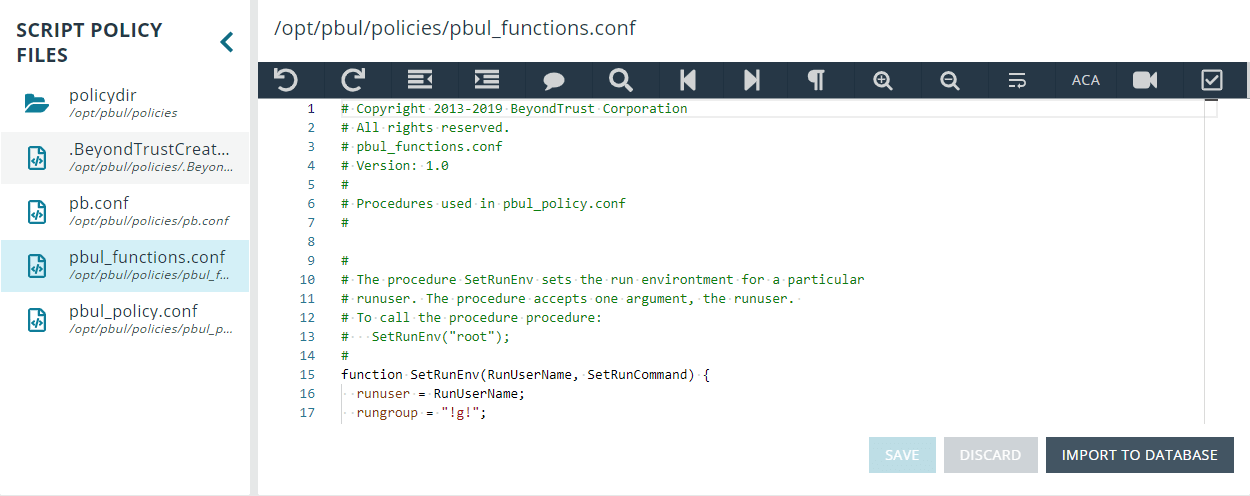
BeyondInsight for Unix & Linux (BIUL) provides an editor component with a number of features to assist with writing code.
- Syntax highlighting
- Line numbering
- Font size control
- Formatting
- Find and replace tools
- Soft wrapping
- Diff tool
Different toolbar options may be available based on the type of script in the editor. Most of the features are available in the toolbar, and keyboard shortcuts can also be used. The editor is used in the Policy Management section where applicable.
Sudo does not support ACA or IOlog playback. The options are not visible in the toolbar when editing a Sudo policy.
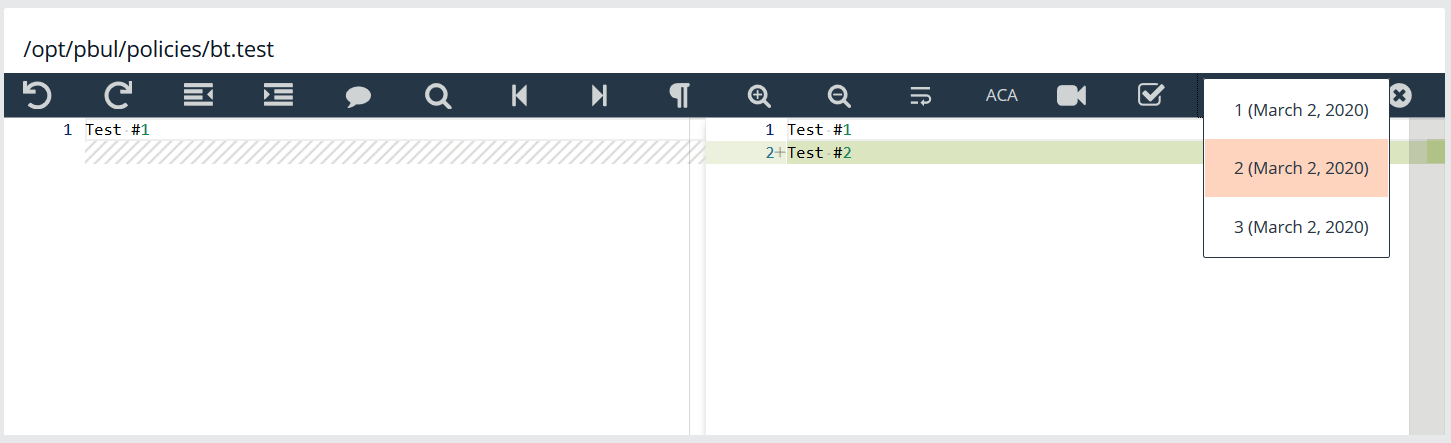
Using the Diff Tool
Use the diff tool to compare different versions of a policy. The policy must have change management turned on and versions of the policy must exist in the database.
To use the diff tool:
- Select the policy, and then click the Versions toolbar button.
- Select a version to compare. The differences are calculated and highlighted. Change the content in the current policy, if needed.
- Click Close Diff Editor.
Version Control
Some policy types support version control. Each time a policy is changed, its version is incremented. The policy with the highest version is the one that is applied.
For policies that support version control, a Versions menu item is available to allow the user to choose a specific version to edit.
Saving a policy makes it the most recent version, which makes it the active policy. Take this into consideration when saving older versions of the files.
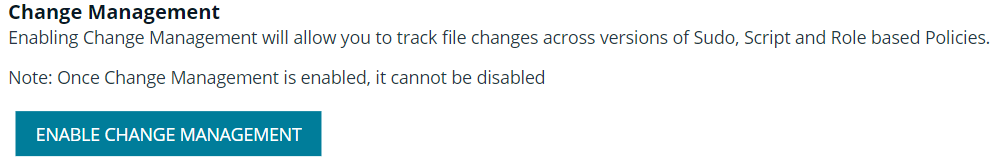
Change Management
BIUL allows users to enable Change Management in the console.
If Change Management is not enabled on the selected server, the option to enable change management is available in the console.
Once Change Management is enabled, it cannot be disabled.
To enable Change Management:
- Go to the Policy page.
- In the Hostname list, select a server entry, and then at the far right, click the vertical ellipsis menu icon and select Configuration.
- Click the Endpoint Privilege Management for Unix and Linux Configuration tab.
- Click the Enable Change Management button.