Daemon Services and Architecture in AD Bridge
The AD Bridge agent is composed of the service manager daemon (/opt/pbis/sbin/lwsmd). At startup, the operating system (OS) is configured to start the service manager daemon. It is then instructed (by the OS) to start all desired services with the command /opt/pbis/bin/lwsm autostart. The service manager daemon keeps track of the services already started and ensures the services are started and stopped in the appropriate order.
The following options are available on the service manager daemon:
/opt/pbis/sbin/lwsmd –help
Usage: /opt/pbis/sbin/lwsmd [options ...]
OPTIONS:
--start-as-daemon Start as a background process
--syslog Log to syslog (default when starting as daemon)
--logfile Log to file
--loglevel <level> Set log level to <level> (error, warning, info, verbose, debug, trace)
--container <group>Start as a container for service group <group>
--ignoresmf Do not start ADBridge daemons using Solaris SMF
--help Show usage information
/opt/pbis/sbin/lwsmd --start-as-daemon --logfile /tmp/log.log
The service manager daemon (/opt/pbis/sbin/lwsmd) includes the following services:
| Service | Description | Dependencies |
|---|---|---|
|
lsass |
Handles authentication, authorization, caching, and idmap lookups. You can check its status or restart it. To view the lsass architecture, see the diagram following the tables. |
netlogon lwio rdr lwreg Usually eventlog. This can be disabled after installation. Sometimes dcerpc. This can be enabled after installation for registering TCP/IP endpoints of various services. |
|
netlogon |
Detects the optimal domain controller and global catalog and caches them. |
lwreg |
|
lwio |
An input-output service used to communicate through DCE-RPC calls to remote computers, such as during domain join and user authentication. |
lwreg |
|
rdr |
A redirector that multiplexes connections to remote systems. |
lwio
lwreg |
|
dcerpc |
Handles communication between Linux or Unix computers and Microsoft Active Directory by mapping data to endpoints. Disabled by default. |
|
|
eventlog |
Collects and processes data for the local event log and can be disabled. |
|
|
lwreg |
The registry service that holds configuration information about both the services and the information provided by the services. |
|
|
reapsysl |
The syslog reaper that scans syslog for events of interest and records them in the eventlog. |
eventlog |
|
usermonitor |
The service scans the system for changes to users, groups, and authorization rights and records the changes in the eventlog. |
lsass eventlog |
| gpagent | Pulls Group Policy Objects (GPOs) from Active Directory and applies them to the computer. |
lsass netlogon lwio rdr lwreg eventlog |
| eventfwd |
Forwards events from the local event log to a remote computer. |
eventlog |
| lwsc |
Smart card service. |
lwpkcs11 |
| lwpkcs11 |
Aids lwsc by supporting PKCS#11 API. |
|
| lwpkcs11r | Smart card redirector service for Windows client. | lwsc |
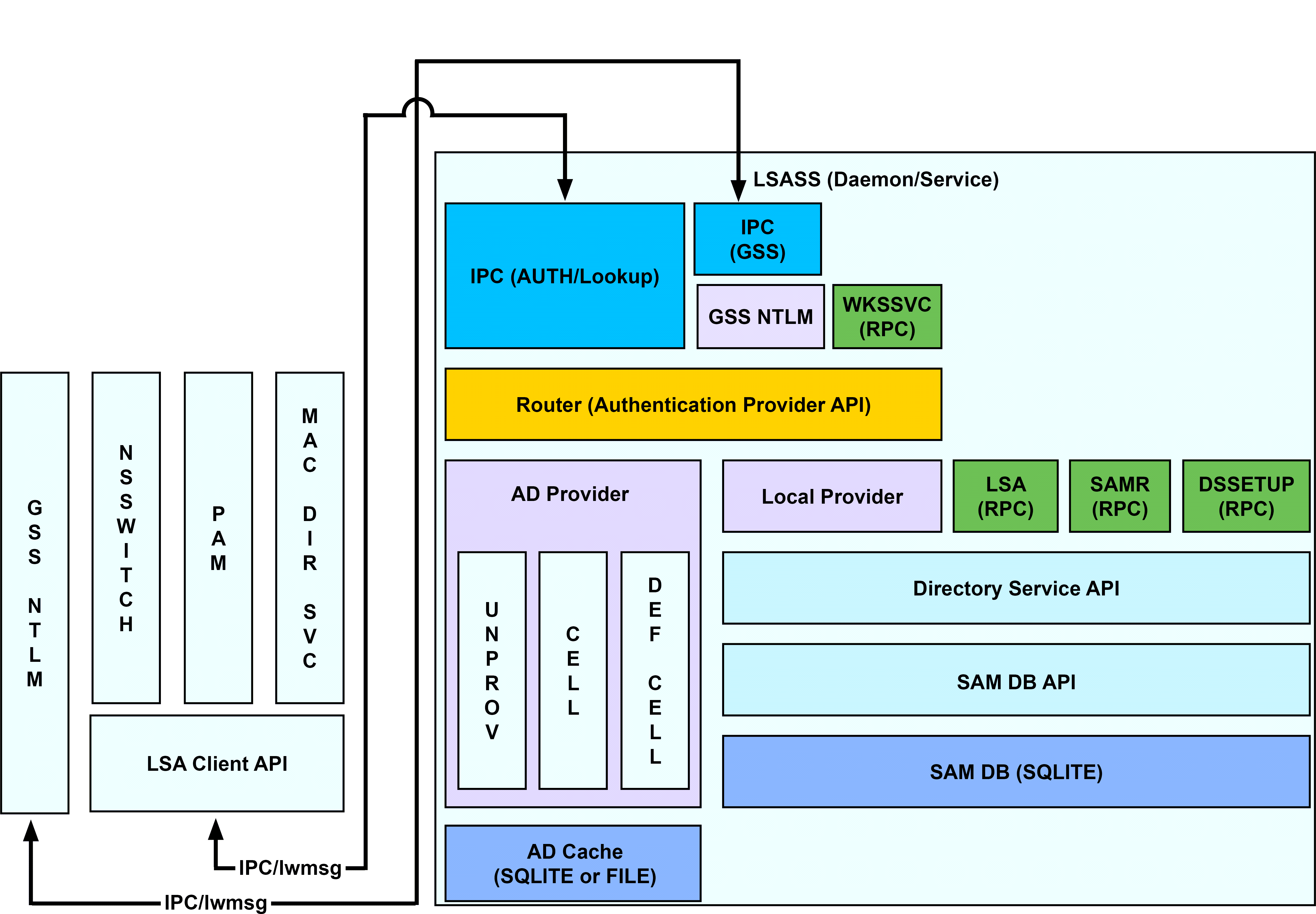
LSASS Architecture
AD Bridge Input-Output Service
The lwio service multiplexes input and output by using SMB1 or SMB2. The service's plugin-based architecture includes several drivers, the most significant of which is coded as rdr, the redirector.
The redirector multiplexes Common Internet File System (CIFS) and Server Message Block (SMB) connections to remote systems. For instance, when two different processes on a local Linux computer need to perform input-output operations on a remote system by using CIFS and SMB, with either the same identity or different identities, the preferred method is to use the APIs in the lwio client library, which routes the calls through the redirector. In this example, the redirector maintains a single connection to the remote system and multiplexes the traffic from each client by using multiplex IDs.
The input-output service plays a key role in the AD Bridge architecture because AD Bridge uses Distributed Computing Environment/Remote Procedure Calls (DCE/RPC). DCE/RPC uses SMB. Thus, the DCE-RPC client libraries use the AD Bridge input-output client library, which in turn makes calls to lwio with Unix domain sockets.
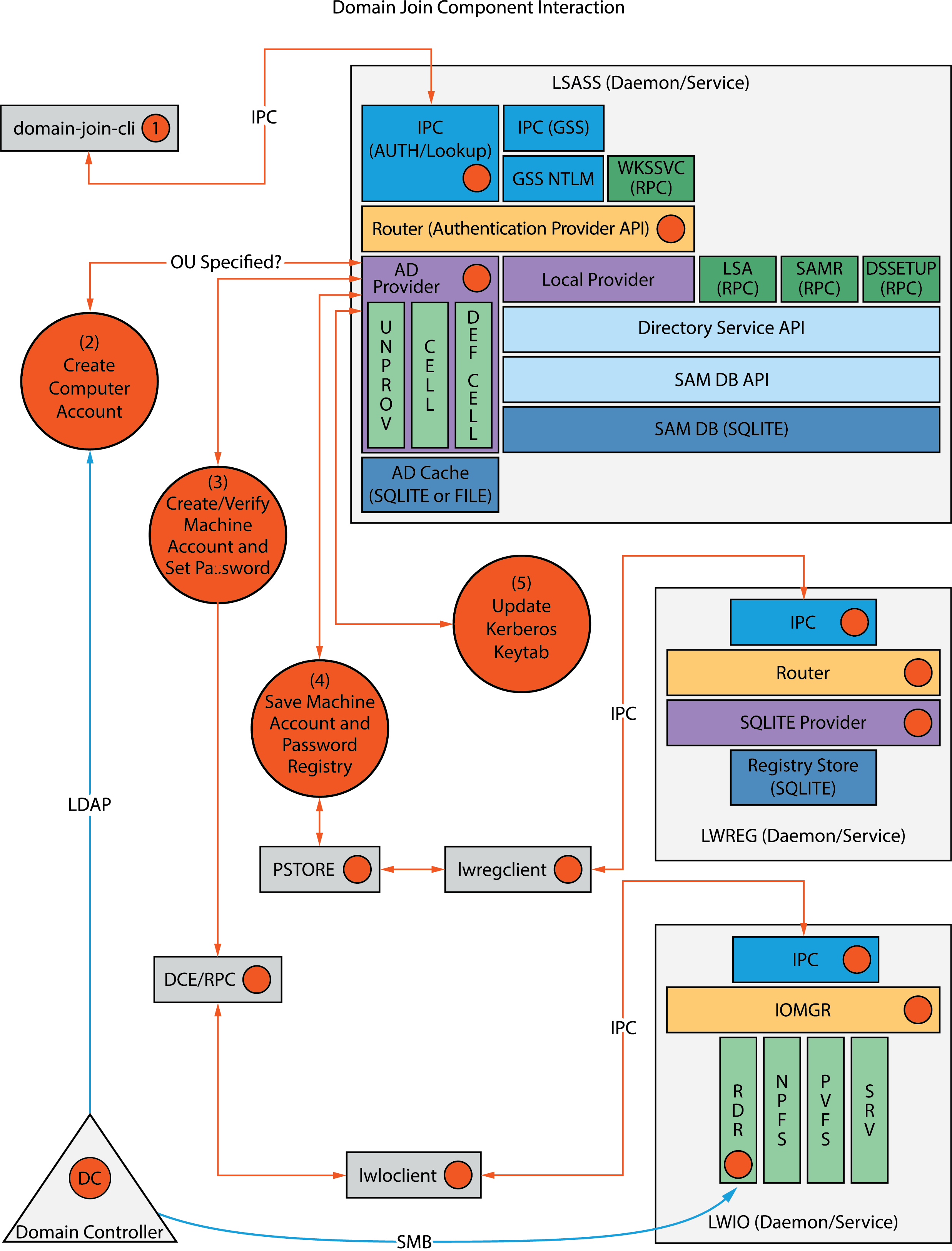
When you join a domain, AD Bridge uses DCE-RPC calls to establish the machine password. The AD Bridge authentication service periodically refreshes the machine password by using DCE-RPC calls. Authentication of users and groups in Active Directory takes place with Kerberos, not RPC.
In addition, when a joined computer starts up, the AD Bridge authentication service enumerates Active Directory trusts by using DCE-RPC calls that go through the redirector. With one-way trusts, the authentication service uses RPC to look up domain users, groups, and security identifiers. With two-way trusts, lookup takes place through LDAP, not RPC.
Because the authentication service registers a trust only when it starts up, you should restart lsass with the AD Bridge Service Manager after you modify a trust relationship.
The AD Bridge Group Policy agent also uses the input-output client library and the redirector when it copies files from the sysvol share of a domain controller.
To troubleshoot remote procedure calls that go through the input-output service and its redirector, use a Wireshark trace or a TCP dump to capture the network traffic.
We recommend Wireshark, a free open-source packet analyzer.
Privileged Access Managment (PAM) Options
AD Bridge uses the following standard PAM options:
- try_first_pass
- use_first_pass
- use_authtok
- debug
Additionally, there are non-standard options to the PAM configuration on some systems:
- unknown_ok: Allows local users to continue down the stack while blocking domain users who do not meet group membership requirements.
- remember_chpass: Prevents the AIX computer on AIX systems, which have both PAM and LAM modules, from trying to change the password twice and prompting the user twice.
- set_default_repository: Used to make sure password changes work as expected on Solaris systems.
- smartcard_prompt: Enables smart card prompts.
- no_require_membership: Allows the require membership check to be skipped.
Manage the AD Bridge Services
Using the AD Bridge Service Manager, you can:
- Track and troubleshoot all the AD Bridge services with a single command-line utility. For example, check the status of the services, view their dependencies, and start or stop them. The service manager is the preferred method for restarting a service, because it automatically identifies a service's dependencies and restarts them in the correct order.
- Use the service manager to set the logging destination and the log level.
For more information, see Manage AD Bridge Services in the AD Bridge Linux Administration Guide.